Nissan K25 LP Throttle Position Sensor Calibration Instructions – Easy
The Nissan K25 LP engine has a throttle position sensor (TPS) to help control how much gasoline is delivered to the engine based on how far the throttle is opened. TPS calibration shows that the sensor and throttle work properly so that the engine runs smoothly.
But sometimes, if your calibration is not correct, the engine cannot respond properly to throttle. This guide will provide the right Nissan K25 LP throttle position sensor calibration instructions.
What Is the Nissan K25 LP Throttle Position Sensor?
The Nissan K25 LP throttle position sensor is a small component that helps control engine performance. It’s connected to the throttle, which opens when you press the gas pedal. The TPS measures how far the throttle opens and delivers the data to the engine’s computer.
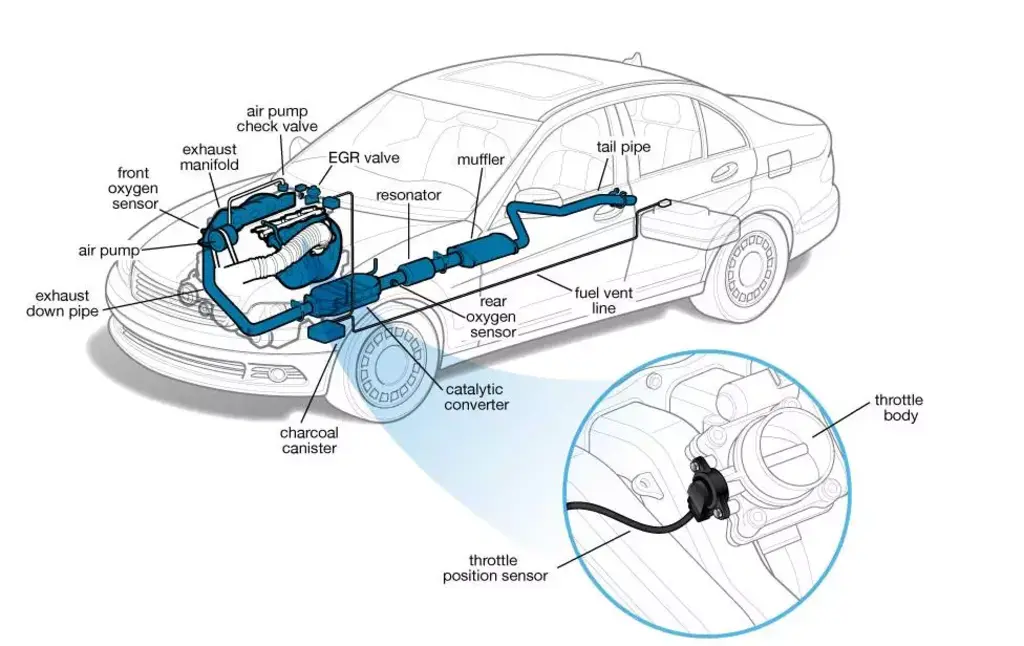
Role of Throttle Position Sensor
TPS is an important part of engine management because it monitors the position of the throttle. It checks how much air enters the engine and continuously measures how much the throttle opens or closes as you press the accelerator pedal. It communicates this data to the engine control unit to adjust the fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture.
The TPS also assists ECU in optimizing engine performance to get smooth acceleration and lower emissions with the help of real-time data. If the TPS is malfunctioning, the ECU could receive inaccurate information. This can cost you more fueling and jerking while you accelerate.
In some situations, the engine could enter “limp mode” as a safety precaution. But don’t worry—regular maintenance and proper calibration of the TPS can keep the engine running smoothly.
3 Types of Throttle Position Sensors
Each type of throttle position sensor has a slightly different design and functionality:
1) Potentiometer-Based TPS
The most common type of TPS is potentiometer-based which measures the position of the throttle using a variable resistor. As the throttle opens or shuts, the sensor’s resistance changes. It gives the engine control unit voltage signals to show the throttle position.
2) Switch-Based TPS
Switch-based TPS design relies on simple on/off switches to know if the throttle is fully open or closed. It does not provide the same level of precision as current potentiometer sensors, but it is nevertheless used in basic applications.
3) Non-contact or Hall Effect TPS
Non-contact or hall effect TPS are advanced enough to detect the throttle position using magnetic fields instead of physical touch. As a result, it is more resilient and less risky to wear and tear than potentiometer-based sensors.
Common Indications That Sensor Is Miscalibrated
To find out if your sensor is miscalibrated, check for these common indications:
1) Engine Hesitation
When the throttle position sensor is incorrectly calibrated, the engine can jerk when you press the gas pedal. This happens when the sensor sends inaccurate information to the engine control unit, which causes fuel delivery delays. As a result, the engine does not respond smoothly and has lag or jerking action while accelerating.
2) Poor Fuel Efficiency
A miscalibrated TPS can cause the engine to use more gasoline than needed. Since the sensor isn’t reliably detecting the throttle position, the ECU can change the air-fuel ratio incorrectly. This inefficiency causes more fuel to be burnt than needed which results in lower miles per gallon and higher fuel expenses over time.
3) Rough Idling
A poorly adjusted TPS can cause rough or uneven idling in which the engine struggles to maintain a consistent RPM. The sensor can transmit incorrect signals, causing the ECU to adjust the throttle position incorrectly. This causes the engine to idle unevenly with variations in RPMs that can cause vibrations or stalling.
4) Check Engine Light
A miscalibrated TPS can turn on the dashboard’s check engine light. The ECU continuously checks the sensor’s signals, and if it finds readings beyond the typical range, it can output an error code. This causes the check engine light to alert the driver about a problem with the throttle or another component in the engine management system.
5 Tools You Need Before Starting Calibration
Here are some important tools you will need before starting the calibration procedure:
1) Digital Multimeter
A digital multimeter is required to measure the TPS’s voltage and resistance. It helps guarantee that the sensor’s readings are accurate and within the manufacturer’s specified range. Using a multimeter, you can check the sensor’s performance before and after calibration and verify that the job is completed correctly.

2) Screwdriver
To modify the TPS, you will need a set of screwdrivers: Phillips or flathead. These tools are required to loosen or tighten the screws that secure the sensor in place. Using the correct size screwdriver prevents damage to the sensor or screws during the calibration process.
3) Vehicle Service Manual
The vehicle service handbook includes TPS calibration instructions unique to your vehicle’s make and model. It will include information such as appropriate voltage ranges and sensor locations. Following the manual will ensure you calibrate accurately according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4) Safety Gloves
Safety gloves protect your hands from dirt and sharp components during calibration. Handling equipment and engine parts without gloves can lead to injury, especially when working in small or uncomfortable locations. Gloves also improve grip and make handling small parts and instruments easier during the procedure.
5) Torque Wrench
A torque wrench is used to tighten the screws and nuts that hold the TPS. Overtightening or under-tightening can result in poor sensor alignment or component damage. A torque wrench helps maintain the proper tension and ensures the sensor is firmly attached without being overstrained.
Safety Precautions
Before starting the whole calibration process, watch out for these precautions:
1) Turn off the Engine
Before starting calibration, check that the engine is turned off. Working on a running engine can result in accidents, such as burns from hot components or injuries from moving parts. Turning off the engine confirms that you work in a safe and controlled atmosphere.
2) Disconnect the Battery
Before working on the throttle position sensor, you must first disconnect the vehicle’s battery. This prevents inadvertent short circuits or electrical shocks while handling electrical components. It also resets the engine control unit and allows the TPS to be properly calibrated when reconnected.
3) Wear Safety Gear
Wearing suitable safety gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, is important for protecting oneself during calibration. Gloves protect your hands from cuts and chemical exposure, whereas safety glasses protect your eyes from debris and unexpected sparks. Wearing the proper gear lowers the risk of injury.
4) Work in Ventilated Areas
Always calibrate in a well-ventilated location, particularly if operating inside. Exhaust fumes from the engine or fuel vapors can accumulate, resulting in dangerous conditions. Proper ventilation creates a safe and breathable environment when working on the car.
5) Use Properly Rated Tools
Make sure that all tools used are correctly rated for automobile work. Using low-quality or inappropriate tools can cause slippage and even human danger. Having the correct tools decreases the likelihood of accidents and ensures that the calibration process runs smoothly and safely.
Nissan K25 LP Throttle Position Sensor Calibration Instructions
It might sound tough but with these steps, you can easily calibrate a Nissan K25 LP throttle position sensor:
- Turn off the engine and unhook the battery to avoid electrical problems.
- Use the handbook to see the precise location of TPS on the Nissan K25 LP engine.
- Reconnect the battery and then connect the multimeter probes to the sensor terminals.
- Turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- Using a screwdriver, loosen the screws that secure the TPS but do not remove them.
- Adjust the sensor until the voltage falls within the required range (0.5-1.0 depending on the manufacturer’s specs).
- Now, check the voltage at the closed throttle to confirm it is within the specified range.
- Start the engine and take the car for a little test drive.
If the car operates smoothly and without problems, the calibration is done correctly.
Conclusion
Knowing the Nissan K25 LP throttle position sensor calibration instructions gives you peace of mind that your engine runs efficiently and reacts smoothly to throttle commands. With our instructions, you can restore normal communication between the sensor and the engine control unit. Remember that proper calibration prevents engine hesitation and other performance concerns caused by a misaligned sensor.
FAQs
What Happens If TPS Is Not Calibrated?
If the throttle position sensor (TPS) is not calibrated, the engine control unit (ECU) will receive inaccurate throttle position information.
What Is a Usual TPS Reading?
In most systems, the voltage reading should be less than 0.7 volts. Open and close the throttle valve numerous times to ensure the steadiness of the growing voltage.
How Do I Reset Nissan Throttle Position Sensor?
To reset a Nissan’s throttle position sensor, detach the battery for 15 minutes. Reconnect and turn the ignition on without starting the engine. Slowly press the accelerator to the floor before releasing it. Turn the ignition off to reset the sensor.






